Chobe National Park
A practical guide to Chobe’s best safari zones (Riverfront, Savuti, Linyanti, Nogatsaa), common wildlife and birds, and a planning map with key gates & hubs.
▶ Table of contents
Quick facts
Best time to visit planner
Choose your travel month
In Chobe, water levels and heat drive where animals concentrate. These suggestions are a solid planning baseline.
Chobe zones cheat sheet
Four distinct ecosystems mean Chobe can feel like “multiple parks in one”.
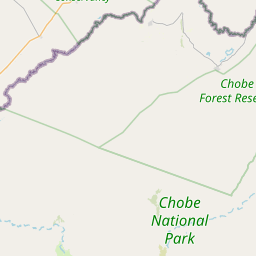
Most accessible area (near Kasane). Great for elephants at the water’s edge, buffalo herds, hippos, crocodiles, and birds.
Classic “sand + predators” safari. Big cats, hyenas, and dramatic scenes. A very different feel from the riverfront.
Remote wetlands/woodlands in the northwest. Strong chance of elephants, predators, and low-traffic drives.
A drier, lesser-known interior section between Savuti and Linyanti—great if you like exploring off the obvious routes.
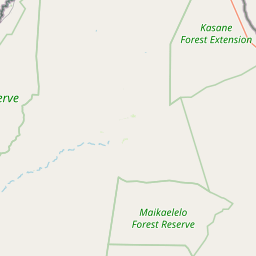
Map (key gates & hubs)









25 Common Animals (non-birds)
African bush elephant
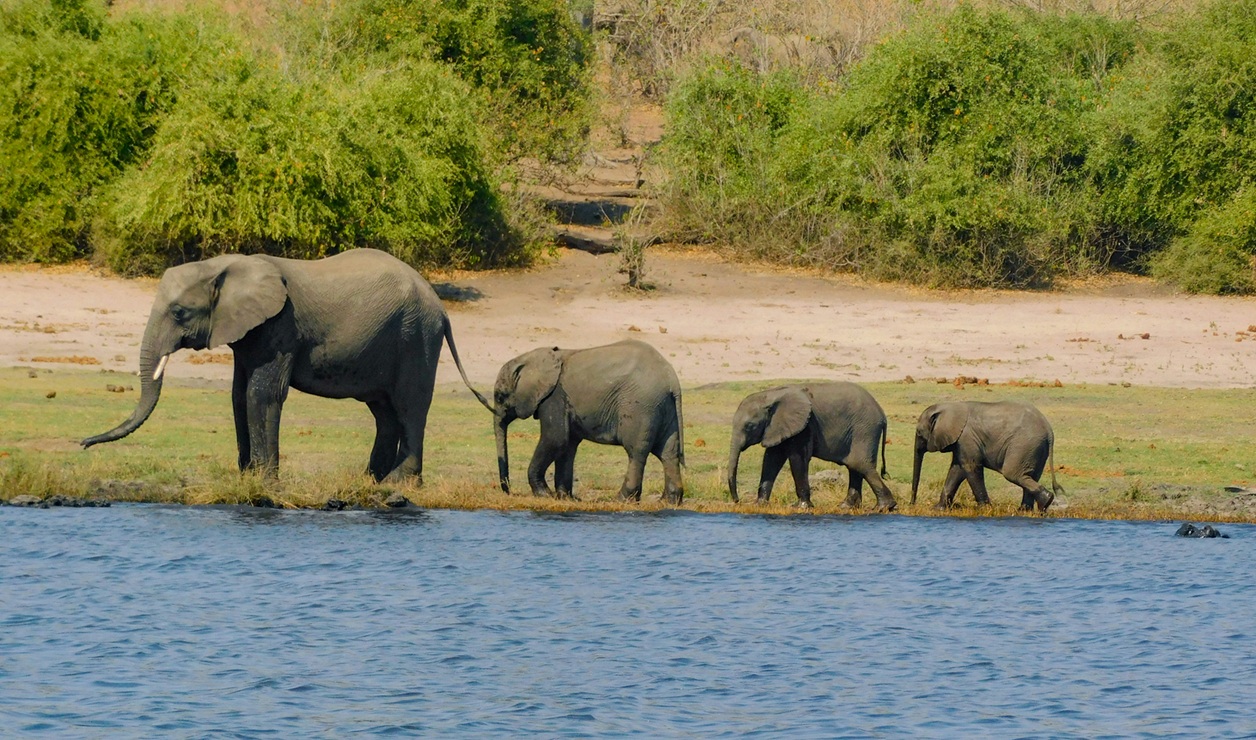
Chobe is famous for elephants—especially along the riverfront in the dry season.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Huge ears, trunk, tusks (vary), family groups near water.
- Male vs female: Adult males are much larger; females live in family herds.
- What it eats: Browser/grazer: leaves, bark, grasses; needs water regularly.
- Where to find it: Riverfront floodplains; Linyanti; woodland edges
- Unique: Large breeding herds often gather at the river—keep respectful distance.
Cape buffalo
Massive herds often appear along the riverfront in the dry season.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Dark heavy body; sweeping horns; tight herds.
- Male vs female: Males have heavier horn bosses; females smaller.
- What it eats: Grazers; prefer grass near water and cover.
- Where to find it: Riverfront floodplains and woodland edges
- Unique: Strong herd defense—predators often target calves.
Lion
Seen in several Chobe zones; Savuti is particularly known for dramatic predator scenes.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Large cat; pride structure; roar at night.
- Male vs female: Males with mane; females smaller.
- What it eats: Predator: buffalo, zebra, wildebeest; scavenges too.
- Where to find it: Savuti; riverfront edges; woodland mosaics
- Unique: Chobe has reports of lions taking elephants (usually young or vulnerable).
Leopard
More secretive; best searched for in riverine woodland and big trees.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Rosette coat; long tail; tree lounging.
- Male vs female: Males larger; females slimmer.
- What it eats: Predator: antelope, monkeys, birds; often caches prey in trees.
- Where to find it: Riverfront woodland; Linyanti thickets; rocky patches
- Unique: Often active at dawn/dusk—scan big branches.
Cheetah
Occasional sightings—open areas and floodplains offer the best chance.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Slim build; tear marks on face; small head.
- Male vs female: Males may form coalitions; females solitary with cubs.
- What it eats: Predator: smaller antelope; prefers daytime hunts.
- Where to find it: Open plains/floodplains (variable)
- Unique: Sprinting hunts are short; overheating limits chase length.
African wild dog
A prized sighting—wild dogs roam widely, so encounters can be sporadic.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Mottled coat; big round ears; pack movement.
- Male vs female: Pack structure; both sexes similar.
- What it eats: Predator: antelope; cooperative hunter.
- Where to find it: Savuti/Linyanti corridors; wide-ranging
- Unique: One of Africa’s most efficient hunters—if you see them, watch quietly and enjoy.
Spotted hyena
Often heard at night; both scavenger and hunter.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Sloping back; spotted coat; ‘laughing’ calls.
- Male vs female: Females larger and dominant.
- What it eats: Opportunistic: hunts and scavenges; bone-crushing jaws.
- Where to find it: Savuti; riverfront edges; den areas
- Unique: Can outlast prey with endurance.
Hippopotamus
Daytime in water; grazes at night—give them space near riverbanks.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Huge barrel body; mostly submerged; yawning displays.
- Male vs female: Males larger and more territorial.
- What it eats: Grazers; short grasses near water.
- Where to find it: Chobe River; channels and pools
- Unique: Boat cruises offer safe, close views—don’t approach on foot.
Nile crocodile
Ambush predator along water edges—watch sandbanks.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Armored back; eyes above water; basking on banks.
- Male vs female: Males larger with heavier head/neck.
- What it eats: Fish, birds, mammals; ambush hunter.
- Where to find it: Chobe River and channels
- Unique: Often seen on boat cruises—especially on sunny sandbanks.
Giraffe (Angolan giraffe)
Often in woodland edges; a favorite on riverfront drives.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Tallest mammal; patchy coat; long neck.
- Male vs female: Males heavier with thicker ossicones; females slimmer.
- What it eats: Browser: leaves (often acacias); long tongue.
- Where to find it: Woodland mosaics; riverfront edges
- Unique: Often seen browsing high branches while other grazers feed below.
Plains zebra
Common on floodplains and open areas; great photo subject at water.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Black-and-white stripes; alert group behavior.
- Male vs female: Stallions defend harems; sexes similar in appearance.
- What it eats: Grazers; can tolerate tougher grasses.
- Where to find it: Riverfront floodplains; open savanna
- Unique: Striping patterns are unique like fingerprints.
Blue wildebeest
Often with zebra; seen in open areas and floodplain edges.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Sloping back; beard; curved horns.
- Male vs female: Males heavier with thicker horns/boss.
- What it eats: Grazer: short to mid grasses.
- Where to find it: Riverfront open areas; savanna patches
- Unique: Herd movement follows grass quality and water availability.
Impala
Graceful antelope—often near woodland edges and riverine zones.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Reddish coat; black rump stripe; males horned.
- Male vs female: Males have lyre-shaped horns; females hornless.
- What it eats: Grazer/browser mix; flexible feeder.
- Where to find it: Riverfront woodland edges; open bush
- Unique: Known for spectacular leaping (up to several meters).
Greater kudu
Shy woodland antelope; look in thicker bush.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Vertical white stripes; big ears; spiral horns (males).
- Male vs female: Males have long spiral horns; females hornless.
- What it eats: Browser: leaves, shoots, pods.
- Where to find it: Woodland and thickets
- Unique: Can vanish into bush—often seen briefly at dawn/dusk.
Waterbuck
Often near water; shaggy coat and distinctive rump ring.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Shaggy grey-brown coat; white rump ring.
- Male vs female: Males have horns; females hornless.
- What it eats: Grazer; prefers grasses near water.
- Where to find it: Near river and marshy edges
- Unique: Strong association with water—good indicator you’re in a riverine zone.
Puku
A wetland antelope—Chobe’s riverfront floodplains are a key place to look.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Golden-brown coat; males with ridged horns.
- Male vs female: Males horned; females hornless.
- What it eats: Grazer: lush grasses near wetlands.
- Where to find it: Riverfront floodplains (localized)
- Unique: In Botswana, puku are strongly associated with the Chobe floodplains.
Warthog
Often trotting with tail up; common on open edges.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Facial ‘warts’; curved tusks; tail up when running.
- Male vs female: Males larger with bigger tusks/warts.
- What it eats: Grazer; digs for roots in dry times.
- Where to find it: Open areas and edges; near burrows
- Unique: Often kneels on front legs while grazing.
Sable antelope
Elegant antelope with long curved horns—more likely away from the busiest riverfront tracks.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Long scimitar horns; strong shoulder; dark coat in males.
- Male vs female: Males darker; both sexes horned.
- What it eats: Grazer/browser mix depending on season.
- Where to find it: Woodland mosaics; Savuti/Linyanti zones (variable)
- Unique: Often prefers slightly quieter woodland away from heavy traffic.
Roan antelope
Big antelope of savanna woodlands—sightings are special.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Grey-brown coat; facial mask; backward-curving horns.
- Male vs female: Males slightly larger; both horned.
- What it eats: Grazer; prefers mid-length grasses.
- Where to find it: Savuti/Nogatsaa interior (variable)
- Unique: Often found in less-visited interior—good reason to explore beyond the riverfront.
Common eland
Largest antelope—sometimes seen in small groups in woodlands.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Large tan antelope; dewlap; spiral horns.
- Male vs female: Males much heavier with thicker neck/dewlap.
- What it eats: Browser/grazer; flexible feeder.
- Where to find it: Woodland/grassland mosaics
- Unique: Despite size, can jump remarkably high.
Chacma baboon
Smart and bold—keep food secured at stops.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Dog-like muzzle; social troops.
- Male vs female: Males larger with heavier build.
- What it eats: Omnivore: fruit, seeds, insects, small animals.
- Where to find it: Riverfront woodland; camps and edges
- Unique: Very adaptable—don’t feed or encourage them.
Vervet monkey
Often around riverine trees and picnic areas.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Grey fur; black face; white fringe.
- Male vs female: Males larger; bright blue scrotum (males).
- What it eats: Omnivore: fruit, leaves, insects.
- Where to find it: Riverfront and camps
- Unique: Excellent alarm calls—watch how other animals react.
Black-backed jackal
Often seen trotting along tracks—opportunistic and alert.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Black ‘saddle’ on back; sharp face; upright ears.
- Male vs female: Males slightly larger.
- What it eats: Omnivore/scavenger: small prey, carrion, insects.
- Where to find it: Open areas and edges
- Unique: Pairs often cooperate to steal scraps from bigger predators.
Banded mongoose
Busy groups in grasses—look for stripy bodies and constant chatter.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Grey-brown with dark bands; moves in groups.
- Male vs female: Similar; social group-living.
- What it eats: Insects, grubs, small vertebrates.
- Where to find it: Grassland edges and termite areas
- Unique: Cooperative breeders—helpers raise the young.
Honey badger
Tough, fearless mustelid—usually a lucky sighting, often near dusk.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Low body; black-and-white ‘cape’ pattern.
- Male vs female: Males larger.
- What it eats: Omnivore: insects, small animals, honey.
- Where to find it: Woodland edges; near dens (variable)
- Unique: Notorious for confidence—keep distance and let it pass.
African civet
Mostly nocturnal; sometimes seen on night drives outside park rules/areas.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Black-and-white banding; low, cat-like body.
- Male vs female: Similar.
- What it eats: Omnivore: small animals, insects, fruit.
- Where to find it: Thickets and riverine zones (mostly at night)
- Unique: Produces ‘civet’ scent used historically in perfumery.
Top 10 Birds
African fish eagle
The voice of African rivers—often seen perched above the Chobe River.
▶ More info
- How to identify: White head and chest; chestnut body; loud calls.
- Male vs female: Females larger.
- What it eats: Fish, waterbirds, carrion.
- Where to find it: Riverfront; big trees near water
- Unique: A signature sound of boat cruises.
Saddle-billed stork
Striking stork with a massive bill—often near shallow water edges.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Huge red/black/yellow bill; tall stance.
- Male vs female: Females have yellow eyes; males dark eyes.
- What it eats: Fish, frogs, small reptiles.
- Where to find it: Floodplains and shallow wetlands
- Unique: A top ‘bucket list’ riverfront bird.
African jacana
Walks on floating plants with long toes—classic wetland sighting.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Long toes; chestnut body; pale face.
- Male vs female: Females larger.
- What it eats: Insects, small aquatic invertebrates.
- Where to find it: Lily pads and calm wetlands
- Unique: Nicknamed the ‘lily-trotter’.
Pied kingfisher
Hovers over the river then dives for fish—easy to spot on cruises.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Black-and-white; hovering dive behavior.
- Male vs female: Males have double breast band; females single band.
- What it eats: Fish.
- Where to find it: Along the river
- Unique: One of the easiest ‘action’ birds to photograph.
Malachite kingfisher
Tiny, brilliant kingfisher—often near reeds.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Bright blue back; orange belly; tiny size.
- Male vs female: Similar.
- What it eats: Small fish, aquatic insects.
- Where to find it: Reedy water edges
- Unique: A jewel-like bird—watch low branches near water.
Goliath heron
Largest heron—often solitary on riverbanks.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Very large heron; chestnut neck; heavy bill.
- Male vs female: Similar.
- What it eats: Fish.
- Where to find it: Riverbanks and channels
- Unique: Slow, deliberate hunting style.
African skimmer
Skims the water surface at dusk—special sighting.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Knife-like bill; flies low with lower mandible in water.
- Male vs female: Similar.
- What it eats: Small fish.
- Where to find it: Wide river channels and sandbanks
- Unique: One of the most distinctive feeding styles in birds.
Southern carmine bee-eater
Bright pink-red bee-eater often in flocks—spectacular on riverbanks in season.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Carmine body; blue-green head; long tail streamers.
- Male vs female: Similar.
- What it eats: Flying insects (bees/wasps).
- Where to find it: Sandy riverbanks; colonies (seasonal)
- Unique: Colony nesting in sandbanks—watch for swarming flights.
Lilac-breasted roller
Color explosion on a branch—often seen on riverfront drives.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Lilac chest; turquoise wings; display flight.
- Male vs female: Similar.
- What it eats: Insects, small lizards.
- Where to find it: Scattered trees; open country
- Unique: Often perches low to spot insects.
Southern ground hornbill
Big black bird on foot—deep booming calls in savanna.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Huge bill; red facial skin; walks in groups.
- Male vs female: Males more blue on throat; females show more red/purple.
- What it eats: Insects, small reptiles, mammals.
- Where to find it: Open savanna with scattered trees
- Unique: Very long-lived; slow breeder.
Top 10 Trees & Signature Plants
Mopane
The ‘butterfly-leaf’ tree—mopane woodland dominates large parts of northern Botswana.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Paired butterfly-shaped leaves; often forms extensive stands.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Woodland (many Chobe zones)
- Unique: Supports mopane worms (seasonal) and many insects/birds.
Baobab
Iconic massive trunk—spectacular silhouette at sunrise/sunset.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Huge swollen trunk; sparse branches.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Rocky/drier pockets
- Unique: Stores water in trunk; long-lived.
Zambezi teak
Hardwood tree associated with the riverfront woodland mosaic.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Tall hardwood; often part of mixed riverfront woodland.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Riverfront woodland (localized)
- Unique: Valued timber species; part of Chobe’s classic hardwood mix.
African teak (Kiaat)
Large deciduous tree; common in parts of northern Botswana.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Spreading canopy; pods; reddish timber.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Woodland mosaics
- Unique: Provides shade and habitat in open woodland.
Leadwood
Dense, dark timber—often stands like a monument in savanna.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Dark rough bark; sturdy trunk; often dead standing trees remain.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Savanna woodlands
- Unique: Hardwood resists decay—dead trees can stand for decades.
Sausage tree
Recognizable by huge sausage-like fruits hanging on long stalks.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Large dangling fruits; compound leaves.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Riverine zones and drainage lines
- Unique: Bats often pollinate the flowers.
Sycamore fig
Big fig tree near water—wildlife magnet when fruiting.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Large spreading fig; clusters of figs.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Riverine areas
- Unique: Figs feed many birds and mammals.
Jackalberry
Large shade tree often near floodplains and riverine zones.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Dense canopy; dark fruits (seasonal).
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Riverine woodland and floodplain edges
- Unique: Fruits attract many birds and mammals.
Marula
Famous for sweet fruits—often attracts wildlife in fruiting season.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Grey bark; broad canopy; fruiting in season.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Savanna woodlands
- Unique: Cultural and ecological importance across southern Africa.
Knobthorn
Savanna thorn tree with distinctive dark ‘knobs’ on branches.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Thorns; dark knob-like swellings on branches.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Savanna woodlands
- Unique: Important browse and perch tree.
Top 10 Flowers & Bushes
Devil’s claw
Ground plant with clawed fruit—most noticed when fruiting.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Low-growing; distinctive hooked fruit.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Sandy soils (localized)
- Unique: Hooks onto animals for dispersal.
Wild sage
Aromatic shrub; leaves release strong scent when crushed.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Aromatic leaves; small clustered flowers.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Roadside edges and bushland
- Unique: Often used as herbal tea in southern Africa.
Aloe (group)
Succulents with flower spikes; various species depending on area.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Fleshy leaves; tall flower stalk.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Drier rocky spots
- Unique: Drought-adapted; stores water in leaves.
African daisy (group)
Many daisies appear after rains—great for macro photos.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Daisy-like blooms; highly seasonal.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Open grassland after rain
- Unique: Peak after rain events.
Lantana
Colorful flower clusters; can form thickets along disturbed edges.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Small multicolored flower clusters; rough leaves.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Edges and disturbed sites
- Unique: Bird-dispersed seeds; invasive in many regions.
Paperbush (Grewia)
Hardy shrub with small flowers and edible fruits in some species.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Star-like flowers; berry-like fruit.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Bushland edges
- Unique: Fruits attract birds; useful browse.
Wire bush
Common roadside herb/shrub with small yellow flowers.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Small yellow flowers; hairy leaves.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Roadside disturbed ground
- Unique: Very hardy; spreads by seed.
Wild hibiscus (group)
Showy blooms may appear after rains depending on area.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Large hibiscus-like petals.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Edges and seasonal drainage lines
- Unique: Attracts pollinators.
Buffalo thorn
Tough savanna shrub/tree—often used by birds for nesting.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Paired thorns; small leaves; edible berries in season.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Savanna woodlands
- Unique: Important browse and shade in dry areas.
Elephant root
Low shrub with large underground root system—often noticed in sandy areas.
▶ More info
- How to identify: Low growth; pods/seed heads; tough rootstock.
- Male vs female: —
- What it eats: —
- Where to find it: Sandy soils in woodland/edges
- Unique: Survives fire and drought via massive root reserves.
Things to do
Sunset boat cruise (Chobe River)
Chobe’s “must-do”. You’ll often see elephants crossing or drinking, hippos and crocodiles, plus close-up birds. Light is best in late afternoon.
Game drives: Riverfront vs Savuti
The Riverfront is easiest and often densest in dry season. Savuti is more remote—great for predators and classic “deep wilderness” vibes.
- Riverfront (Kasane side): elephants, buffalo, hippos + birds
- Savuti: lions, hyenas, wild dog (luck), dramatic sightings
- Linyanti: quiet drives + strong elephant and predator potential
Self-drive notes
Riverfront day drives from Kasane are realistic. Savuti and Linyanti are usually 4×4 territory with deep sand and longer distances.
Combine with Victoria Falls
Kasane is a popular base for combining Chobe with Victoria Falls. Many itineraries do Chobe as a 1–2 day highlight and add Falls before/after.
FAQ
Best time to visit Chobe?
For the riverfront, dry season (roughly May–October) often gives the most concentrated sightings along the Chobe River. Green season can be lush and quieter, with excellent birding and dramatic skies.
Is Chobe good for elephants?
Yes—Chobe is famous for large elephant concentrations, especially along the riverfront in the dry season.
Do I need a 4×4?
For Riverfront day drives from Kasane, many travelers use standard safari vehicles (or guided tours). For Savuti/Linyanti, a proper 4×4 is usually required due to deep sand and remote conditions.
How to do Chobe in 1 day?
Morning Riverfront game drive + afternoon sunset boat cruise is the classic “best of Chobe” day plan.
- Most Booked Safari Lodges in Africa (2026)
- Sabi Sand Safari Guide: Best Time to Go, Wildlife, Tours & Tips (2026 Guide)
- Top 10 Beach Hotels in Namibia (2026 guide)
- Masai Mara National Reserve Complete Guide: Map, Junctions, Wildlife, Picnic Sites & Tips (2026)
- Top 10 South Africa Coastal Hotels with Kitchenettes (2026 Guide)
Share with others which spots are the best to find which animals in the comments below!

























































Leave a Reply